To smooth the process, we've put together this Complete Your UK Self Assessment Tax Return: Essential Steps For Filing Accuracy guide to help you make the right decision.
| Key differences | Key takeways |
|---|---|
| Self Assessment is a system of taxation in the UK that allows individuals to declare their income and pay their taxes directly to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). | |
| You need to file a Self Assessment tax return if you're self-employed, a sole trader, or a partner in a business. | |
| The deadline for filing a Self Assessment tax return is 31st January following the end of the tax year. | |
| You can file a Self Assessment tax return online or by post. | |
| If you make a mistake on your Self Assessment tax return, you should contact HMRC as soon as possible. |

File Your Self-Assessment Tax Returns Before The Deadline! - Source www.ukpropertyaccountants.co.uk
FAQ
To ensure complete accuracy, read Complete Your UK Self Assessment Tax Return: Essential Steps For Filing Accuracy which covers common mistakes and provides essential guidance for successful tax return submission.
Do you need to file a self-assessment tax-return this month? - Source www.msn.com
Question 1: Can I file my tax return late without penalties?
No, late filing carries a £100 penalty. File on time, even if you cannot pay the tax immediately.
Question 2: Do I need to keep receipts for my expenses?
Yes, keep receipts for all business-related expenses. They can be requested during an HMRC audit.
Question 3: Can I claim expenses for using my home as an office?
Yes, you can claim a portion of household expenses, such as rent, utilities, and internet, as long as you regularly work from home.
Question 4: What happens if I make a mistake on my tax return?
Contact HMRC immediately for guidance. Submit an amended return as soon as possible to avoid penalties.
Question 5: What if I cannot pay my tax bill?
Contact HMRC to set up a payment plan. Failure to pay can result in fines and legal action.
Question 6: Do I need to register as self-employed to file a tax return?
Yes, you must register with HMRC as self-employed to file a tax return. Failure to register can result in penalties.
Filing an accurate tax return is crucial for avoiding penalties and ensuring compliance. Seek professional advice if necessary and always refer to the official HMRC website for the latest guidance.
Continue reading for more helpful information and strategies for successful tax return submission.
Tips
Filing an accurate Self Assessment tax return is crucial to ensure a correct tax calculation. Here are some essential tips to achieve filing accuracy:
Tip 1: Gather Essential Documents: Before starting your return, gather all relevant documents, including P60s, P11Ds, bank statements, and any other income or expenses records.
Tip 2: Understand Taxable Income and Allowances: Determine which types of income are taxable and identify any applicable allowances, such as the personal allowance, to reduce taxable income.
Tip 3: Claim Deductions and Reliefs: Explore legitimate deductions and reliefs available to reduce tax liability, such as expenses related to employment or charitable donations.
Tip 4: Declare All Income: Ensure you declare all income sources, including employment, self-employment, property rental, and investments.
Tip 5: Check for Errors: Carefully review your return before submission to identify and correct any errors in calculations or omissions.
Tip 6: File on Time: Adhere to the deadlines set by HMRC to avoid late filing penalties.
By following these tips, you can significantly improve the accuracy of your Self Assessment tax return and ensure compliance with HMRC regulations.
Complete Your UK Self Assessment Tax Return: Essential Steps For Filing Accuracy
Self Assessment Tax Return (SATR) filing precision is crucial for UK taxpayers. Here are 6 key aspects to ensure accuracy:
- Accurate Record Keeping: Meticulously maintain expenses, income, and other financial data throughout the tax year.
- Obtain Tax Code: Verify your tax code from HMRC to determine the amount of tax deducted at source.
- Understand Allowances and Deductions: Identify and claim eligible allowances and deductions to reduce your tax liability.
- Submit on Time: Avoid penalties by submitting your SATR before the January 31st deadline.
- Use Software or Accountant: Consider using tax software or consulting an accountant for assistance with complex returns.
- Keep Records: Retain all supporting documentation for at least 22 months after filing.
These aspects are interconnected. Accurate record keeping provides a solid foundation for calculating your tax liability. Understanding your tax code ensures you pay the correct amount of tax. Allowances and deductions reduce your tax burden. Timely filing avoids penalties. Tax software or accountants can enhance accuracy. Lastly, keeping records allows for future reference and potential HMRC inquiries.
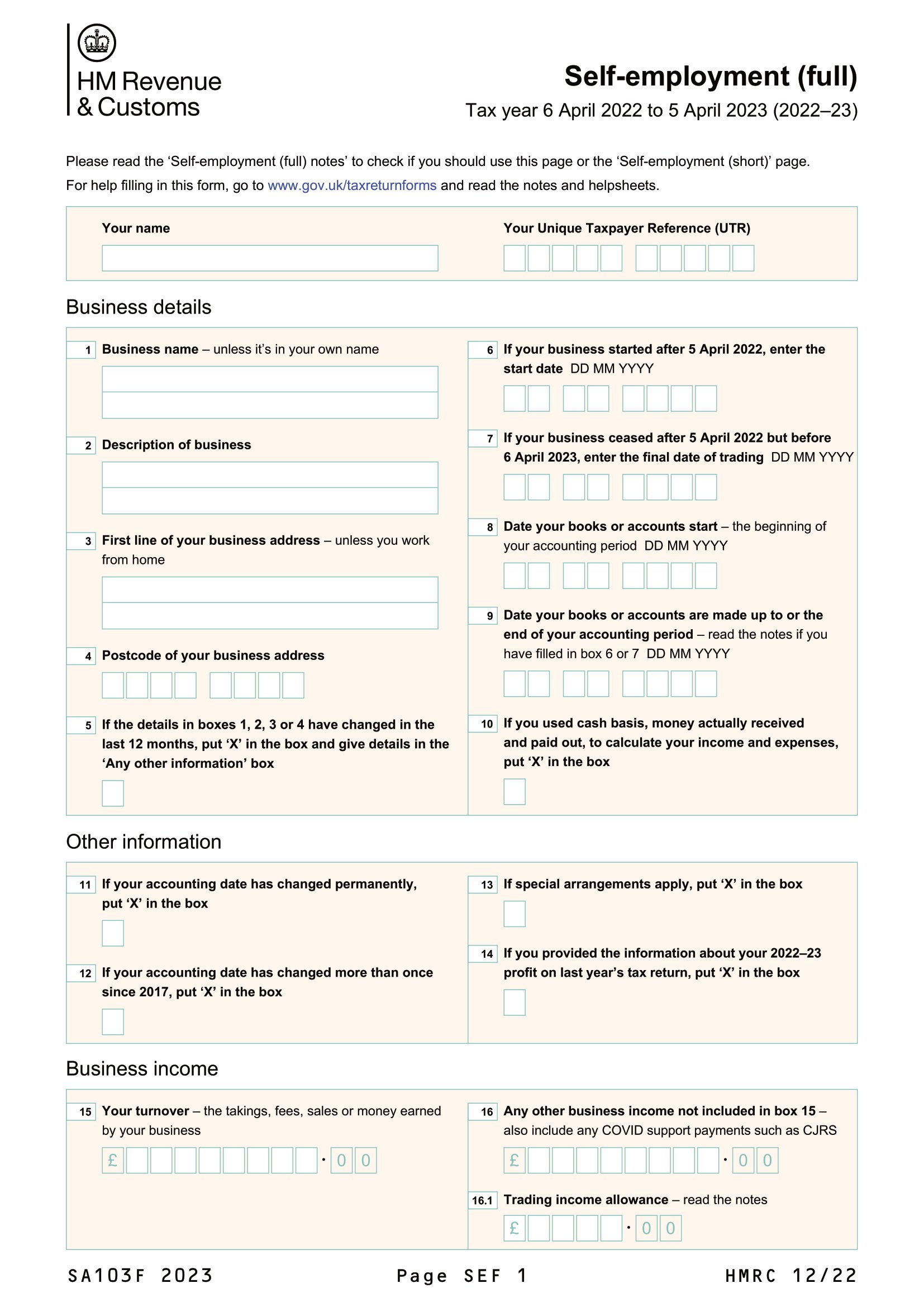
Self-Employed Tax Return in the UK: A Step-by-Step Guide - Health - Source healthandwealthalerts.com
Complete Your UK Self Assessment Tax Return: Essential Steps For Filing Accuracy
Filing a complete and accurate UK Self Assessment Tax Return is crucial for individuals who are self-employed or have additional income beyond their main employment. The process involves declaring all taxable income, claiming allowable expenses, and calculating the tax liability. Filing accurately ensures compliance with HMRC regulations and avoids potential penalties or investigations. Understanding the essential steps for filing accuracy is essential for fulfilling this obligation effectively and efficiently.
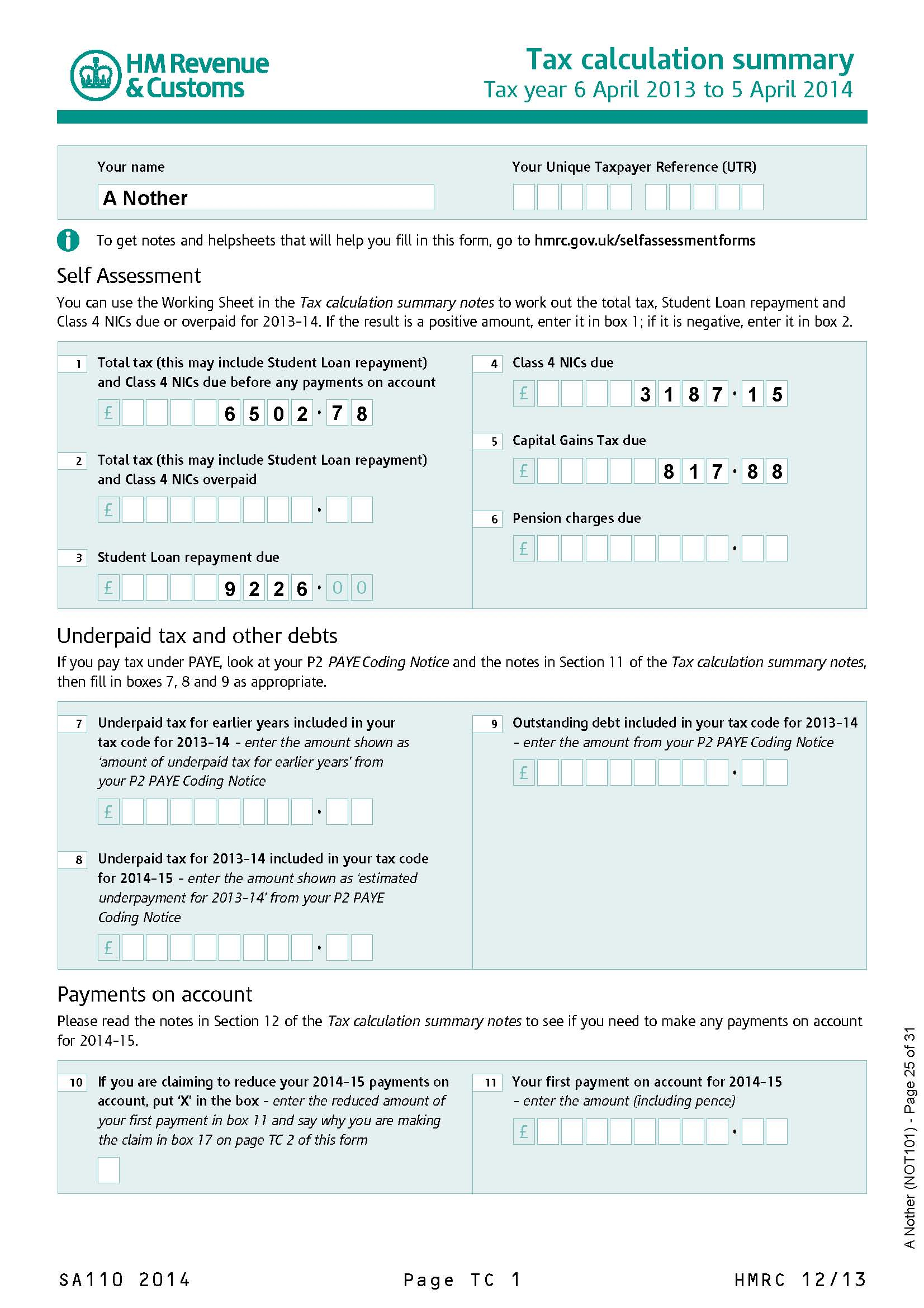
Self Assessment Tax Return Form Employment Pages - Employment Form - Source www.employementform.com
The UK Self Assessment Tax Return comprises several sections that require careful attention. Box 1 includes employment and pension income, while Box 2 covers other income sources such as property or self-employment. Box 3 deals with savings and investments, and Box 4 includes dividends, interest, and any other taxable income. Expenses and allowances are claimed in the relevant sections, and the net income is then calculated. Deducting allowable expenses reduces the taxable income, leading to a lower tax liability. Properly classifying expenses as allowable ensures accuracy and avoids potential disputes with HMRC.
Completing the Self Assessment Tax Return can be challenging, especially for individuals with complex financial arrangements or those who are self-employed. Seeking professional advice from an accountant or tax advisor can provide valuable assistance in navigating the process and ensuring accuracy. They can help identify allowable expenses, optimize tax savings, and minimize the risk of errors or omissions. Additionally, utilizing HMRC's online resources, webinars, and guidance can provide clarity and support throughout the filing process.
Filing an accurate Self Assessment Tax Return is not only a legal obligation but also a means of securing financial stability and peace of mind. By following the essential steps and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can ensure compliance, avoid penalties, and optimize their tax position. Regular reviews of the tax code and keeping up-to-date with relevant legislation are recommended to maintain accuracy and remain informed of any changes or updates.
Essential Steps for Filing Accuracy:
| Collect all necessary documents and information. |
| Understand the different sections of the tax return and the corresponding income and expense categories. |
| Identify allowable expenses and ensure they are properly classified. |
| Calculate the net income and tax liability accurately. |
| Double-check all calculations and ensure there are no errors or omissions. |
| Submit the tax return on time to avoid penalties or late filing fees. |

