Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Geological Marvel And Seismic Hazard.
Through extensive analysis and research, we have assembled this comprehensive guide to shed light on the complexities of the San Andreas Fault and its profound implications for the region. By delving into its geological origins, seismic history, and ongoing scientific monitoring, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of this fascinating yet formidable natural phenomenon.
| Feature | Explanation |
| ----------- | ----------- |
| Formation | Approximately 30 million years ago, tectonic forces created the San Andreas Fault as the boundary between the Pacific and North American plates. |
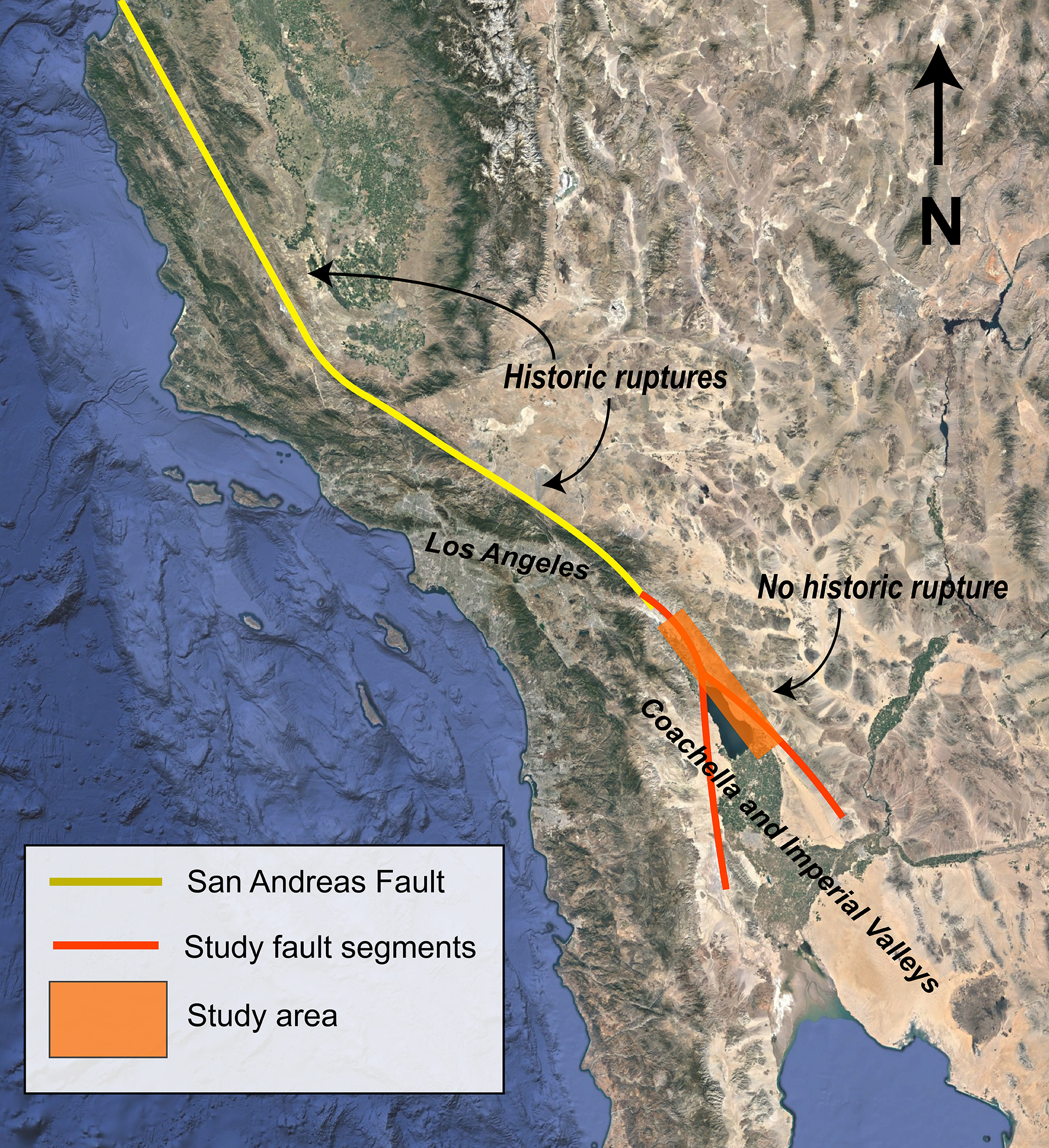
| Length and Location | Stretching approximately 750 miles through California, from Cape Mendocino to the Salton Sea, the fault divides the state into two distinct geological provinces. |
| Seismic Activity | The San Andreas Fault is renowned for its history of significant earthquakes, including the devastating 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake. |
| Hazard Mitigation | Extensive scientific monitoring, building codes, and emergency preparedness measures are crucial for mitigating the risks associated with potential earthquakes. |
- Geological Origins and Formation
- Seismic History and Notable Earthquakes
- Monitoring and Hazard Assessment
- Earthquake Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
- Impact on California's Landscape and Infrastructure
- Ongoing Scientific Research and Collaborations
FAQ
Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Geological Marvel And Seismic HazardUnveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Geological Marvel And Seismic Hazard provides comprehensive information on the San Andreas Fault, including its formation, characteristics, and seismic activity. This FAQ section addresses common questions and misconceptions regarding this intriguing geological feature.
Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Journey Through An Interactive Map - Source mapofaravaipacanyon.pages.dev
Question 1: What is the San Andreas Fault?
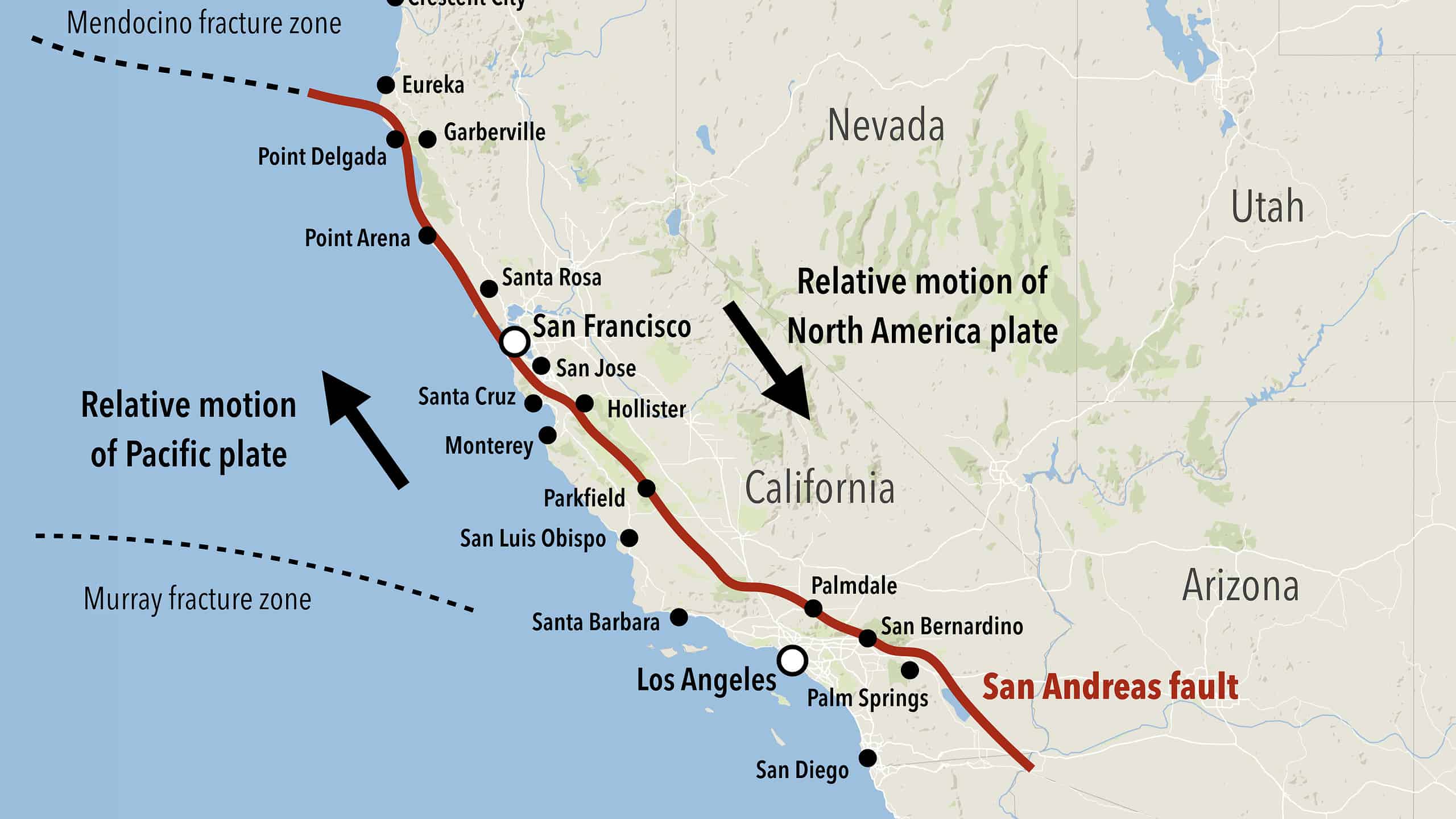
The San Andreas Fault is a transform fault that runs approximately 1,300 kilometers through California. It marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and the relative motion between these plates generates significant seismic activity.
Question 2: How did the San Andreas Fault form?
The San Andreas Fault is a result of the interaction between the Pacific and North American Plates. As the Pacific Plate moves northwestward relative to the North American Plate, the fault provides a release point for the accumulated strain.
Question 3: What are the main characteristics of the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault is a right-lateral strike-slip fault, meaning that the two sides of the fault move horizontally past each other. It is characterized by a complex system of fault segments and branches, extending from the Salton Sea in the south to Cape Mendocino in the north.
Question 4: Is the San Andreas Fault still active?
Yes, the San Andreas Fault is still active, and it continues to produce earthquakes. The fault has a history of producing large earthquakes, including the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
Question 5: What are the seismic hazards associated with the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault poses a significant seismic hazard to the densely populated areas of California. Earthquakes along the fault can cause ground shaking, liquefaction, landslides, and tsunamis. It is crucial to prepare for potential earthquakes and to take appropriate mitigation measures.
Question 6: What are the long-term implications of the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault will likely continue to be active for millions of years. As the Pacific and North American Plates continue to move relative to each other, the fault will continue to accumulate strain and generate earthquakes. Understanding the fault's characteristics and seismic hazards is essential for planning and disaster preparedness.
The San Andreas Fault is a complex and dynamic geological feature that poses significant seismic hazards. By understanding the fault's formation, characteristics, and seismic activity, we can better prepare for potential earthquakes and mitigate their impacts.
For more detailed information on the San Andreas Fault, refer to the article Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Geological Marvel And Seismic Hazard.
Tips for Understanding the San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a fascinating geological feature, yet it also poses a significant seismic hazard. By understanding the fault and its potential risks, communities and individuals can better prepare for future earthquakes.
Tip 1: Learn about the fault's history and structure.
Understanding the San Andreas Fault's history and structure provides valuable insights into its behavior. This includes studying past earthquakes, examining the fault's surface features, and utilizing geophysical techniques to map its subsurface extent.
Tip 2: Monitor seismic activity along the fault.
Monitoring seismic activity along the San Andreas Fault is crucial for detecting potential earthquakes. Seismographs and other instruments can measure ground motion, helping to identify and locate earthquakes, as well as providing early warning systems in case of a major event.
Tip 3: Evaluate the seismic hazard in your area.
Assessing the seismic hazard in your area is essential for risk mitigation. This involves determining the likelihood and potential magnitude of earthquakes, considering local geology, fault proximity, and building codes. Hazard maps and resources from geological surveys can provide valuable information.
Tip 4: Implement earthquake preparedness measures.
Earthquake preparedness measures can significantly reduce the risks associated with the San Andreas Fault. This includes reinforcing structures, securing furniture, developing emergency plans, and stockpiling essential supplies. Educating oneself and the community about earthquake safety is also crucial.
Tip 5: Consider retrofitting buildings in vulnerable areas.
For buildings located in highly vulnerable areas, seismic retrofitting measures can be considered. These involve structural modifications to strengthen buildings and reduce the risk of collapse during an earthquake. Professional engineers can evaluate the need for and design appropriate retrofitting solutions.
Tip 6: Participate in community preparedness programs.
Community preparedness programs play a vital role in disaster readiness. Local organizations and governments often conduct drills, workshops, and outreach programs to educate residents about earthquake hazards and response protocols. Participating in these programs helps foster a sense of community and facilitates efficient response and recovery.
These tips can assist individuals and communities in understanding the San Andreas Fault and mitigating the risks associated with it. By staying informed, implementing preparedness measures, and fostering collaboration, we can enhance our resilience and ensure a safer future.
Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Geological Marvel And Seismic Hazard
The San Andreas Fault is a complex and dynamic geological feature that plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape of California and poses significant seismic hazards. Understanding its various aspects is essential for earthquake preparedness and hazard mitigation.
- Transform Boundary: The fault marks the boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates, where they slide past each other horizontally.
- Seismic Activity: The fault is responsible for numerous earthquakes, including the devastating 1906 San Francisco earthquake, and is a major source of seismic hazard for the region.
- Geologic History: The fault has a long and complex geologic history, with evidence of major earthquakes occurring over millions of years.
- Landscape Formation: The fault's movement has shaped the topography of California, creating mountain ranges, valleys, and other geologic features.
- Earthquake Preparedness: Understanding the fault's behavior and potential hazards is crucial for earthquake preparedness and risk reduction.
- Scientific Research: The San Andreas Fault is a natural laboratory for studying earthquake processes and developing earthquake prediction and mitigation techniques.
These aspects highlight the significance of the San Andreas Fault as a geological marvel, a source of seismic hazards, and a subject of ongoing scientific research. Its study and understanding are essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of communities in earthquake-prone regions like California.
Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Journey Through An Interactive Map - Source mapofaravaipacanyon.pages.dev
Unveiling The San Andreas Fault: A Geological Marvel And Seismic Hazard
The San Andreas Fault is a 1,300-kilometer-long fault system that runs through California. It is the most famous fault in the world and is responsible for some of the largest earthquakes in history. The fault is a geological marvel, but it also poses a significant seismic hazard to the millions of people who live near it.

Download These Printable Earthquake Word Games. | San andreas fault - Source www.pinterest.com
The San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault, which means that the two sides of the fault move horizontally past each other. The fault is part of the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The Pacific Plate is moving northwestward relative to the North American Plate, and this movement is what causes the earthquakes.
The San Andreas Fault is a major source of seismic activity in California. The fault has produced some of the largest earthquakes in history, including the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. These earthquakes caused widespread damage and loss of life.
The San Andreas Fault is a geological marvel, but it also poses a significant seismic hazard. Scientists are working to better understand the fault and to develop ways to mitigate the risk of earthquakes.
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Movement of the Pacific Plate relative to the North American Plate | Earthquakes |
| Earthquakes | Damage and loss of life |
Conclusion
The San Andreas Fault is a complex and fascinating geological feature. It is a reminder of the power of nature and the importance of being prepared for earthquakes. Scientists are working to better understand the fault and to develop ways to mitigate the risk of earthquakes.
There are a number of things that can be done to reduce the risk of earthquake damage. These include:
- Building earthquake-resistant structures
- Retrofitting existing structures to make them more earthquake-resistant
- Developing early warning systems
- Educating the public about earthquake preparedness
By taking these steps, we can help to reduce the risk of earthquake damage and protect our communities.
